Usage
Run this command in your terminal to list files in the current directory:
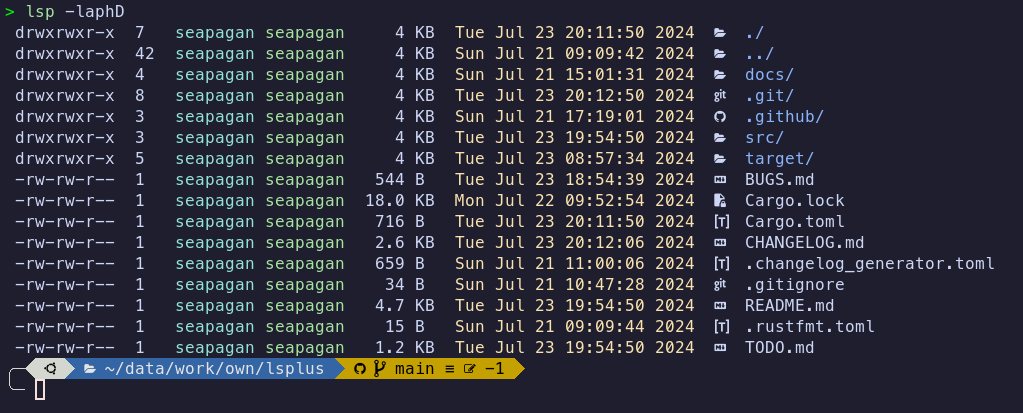
lsp <options> <path | file>
Both the options and the path are optional. If no path is provided, the current
directory will be listed. If no options are provided, the default options will
be used which are similar to the ls command.
Curently, only a sub-set of the standard ls options are supported. These are:
-a/--all- Show hidden files-A/--almost-all- Show hidden files, but don't show.and `..-p/--slash-dirs- Append a '/' to directories-l/--long- Show long format listing-h/--human-readable- Human readable file sizes-D/--sort-dirs- Sort directories first--no-icons- don't show file or folder icons-Z/--fuzzy-time- Show fuzzy time for file modification times
You can combine the short options together, e.g. -laph will show a long format
listing with hidden files, append a '/' to directories, and show human-readable
file sizes.
Use the --help option to see the full list of options.
The long-format listing is currently colorized by default and cannot be
disabled. This will be made configurable in the future along with adding more
of the original ls options.
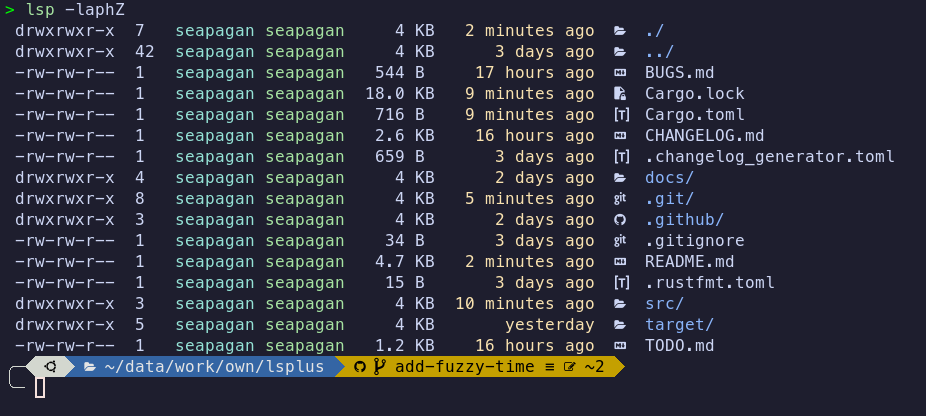
Fuzzy Time
The -Z option will show a fuzzy time for file modification times. This will
show the time in a human-readable format, e.g. '2 hours ago', 'yesterday', etc.
Icons
Icons are added to folders, files, and links. There is only a limited set of mappings implemented at the moment, but more will be added in the future. Add an issue if you have a specific icon you would like to see - even better, add a Pull Request implementing it! :grin:
You can disable the icons by using the -no-icons option.
Aliases
The lsp command can be aliased to ls by adding the following line to your
.bashrc, .zshrc or similar file:
alias ls='lsp'
You will need to restart your shell or source your configuration file for the alias to take effect.
The example below shows an alias for ls that uses many of the current options:
alias ll='lsp -laph'
This will show a long format listing with hidden files, append a '/' to directories, and show human readable file sizes.
You can also use the configuration file to set the default options you want.
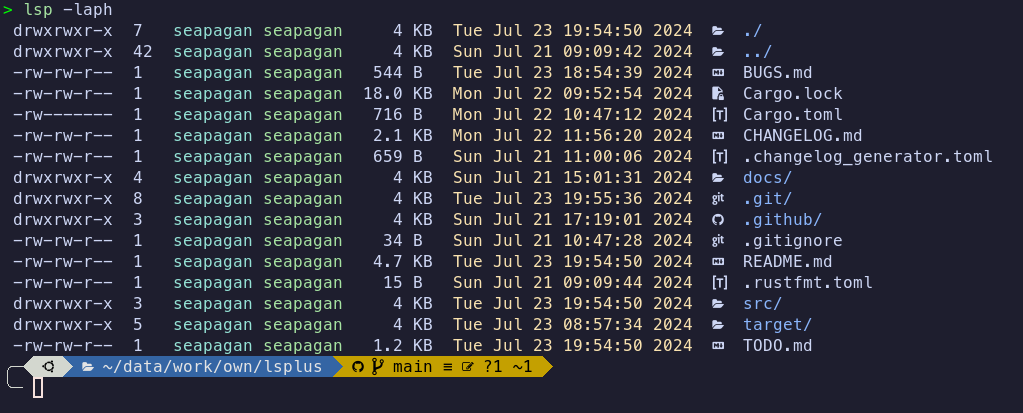
If you add the '-D' option to the command, directories will be sorted first: